Introduction
Prerequisites: Graph Theory, Depth First Search
A topological sort or topological order of a directed graph is an order in which every node comes after its ancestors.
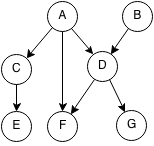
For example topological orders could be:
- (A, B, C, D, E, F, G)
- (B, A, D, C, F, E, G)
- (B, A, D, G, F, C, E)
But (B, A, C, F, D, E, G) is not a topological ordering because D is an ancestor of F and it comes after F.
Implementation
Topological sort can implemented in O(n) time using DFS for a directed acyclic graph (a digraph with no cycles). How it works:
- Start with an empty top order.
- Pick any unmarked node.
- Get the DFS preordering from that node for unvisited nodes.
- Add the DFS to the head of the current order.
- Mark every node that has been visited.

Example:
- Pick C
- DFS preorder from C is (C,E)
- Add DFS preorder to head [C,E]
- Pick F
- DFS preorder from F is (F)
- Add DFS preorder from F to head [F,C,E]
- Pick B
- DFS preorder from B is (B,D,G)
- Add DFS preorder from B to head [B,D,G,F,C,E]
- Pick A
- DFS preorder from A is (A)
- Add DFS preorder from A to head [A,B,D,G,F,C,E]
- Done, all nodes visited
A DFS order from a node is guaranteed to be a topological order. Since we add everything to the head of the order, a child of a node cannot appear before it.