Introduction
A vector is a stack that is implemented as an array. It is very similar to an array, but it is more flexible in terms of size. Elements are added and removed only from the end of the array. When more elements are added to the vector and the vector is at full capacity, the vector resizes itself and reallocates for 2*N space. When using an vector we can keep adding elements and let the data structure handle all the memory allocation.
| Operation | Get | Push | Pop | Insert |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time Complexity | O(1) | O(1) | O(1) | O(n) |
Class
There is a builtin Vector class already, but we will go through the implementation of a simple integer vector class to understand how the data structure works.
In our vector class, we need to store the element and the size of the current vector.
public class Vec {
private int[] arr;
int size = 0;
public Vec(int size) {
arr = new int[size];
}
}
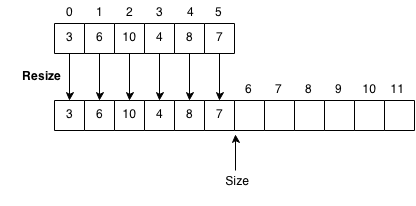
Resize
Resize will be used to resize the array to have twice the capacity. We create a new array of two times the size of the old one and copy the old elements over.
public void resize() {
int[] newArr = new int[2 * arr.length];
// Copy to new array.
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
newArr[i] = arr[i];
}
arr = newArr;
}
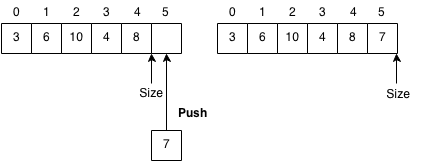
Add Element
Add element will add elements to the end of the vector. If the array is full, the vector will resize itself.
public void add(int x) {
if (size >= arr.length) {
resize();
}
arr[size] = x;
size++;
}
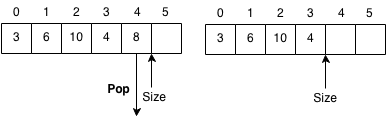
Pop
Removes the element at the end of the vector. We decrease the size of the vector and return the last element.
public int pop() {
if (size == 0) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
int ret = arr[size];
size--;
return ret;
}
Remove
Removes element at index and shifts all elements to the right of it to the left by one.

public int remove(int idx) {
if (idx < 0 || idx >= size) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
int ret = arr[idx];
while (idx + 1 < size) {
arr[idx] = arr[idx + 1];
idx++;
}
size--;
return ret;
}
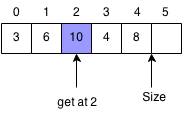
Get Element
Returns the element at the specified index. It will throw an exception if the index is out of bounds.
public int get(int idx) {
if (idx < 0 || idx >= size) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
return arr[idx];
}
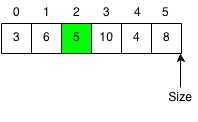
Insert Element
Insert the new number x at the index.
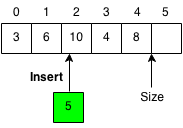
We need to make space for the new element so when we insert the element, we have to shift all the elements to the right of the index by 1.
public void insert(int idx, int x) {
if (idx < 0 || idx > size) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
size++;
if (size >= arr.length) {
resize();
}
int idx2 = size;
// Shift elements to the right.
while (idx2 > idx) {
arr[idx2] = arr[idx2 - 1];
idx2--;
}
// Insert element.
arr[idx] = x;
}
Exercises
- Implement add(Vector v) to the Vector class, which adds all the elements of v to the current vector.
- Implement remove(Integer i) that finds the element i and removes it from the current vector.