Introduction
An adjacency list stores a graph in an array of linked lists. Each node stores its neighbours by keeping a linked list of edges. Adjacency lists are slower when checking if an edge exists but they are more memory efficient since they only need to store the total number of edges.
Example:
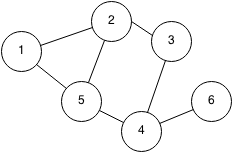
The adjacency list of the graph is:
| Node | edges |
|---|---|
| 1 | 2 5 |
| 2 | 1 3 5 |
| 3 | 2 4 |
| 4 | 3 5 6 |
| 5 | 1 2 4 |
| 6 | 4 |
Implementation
Here is a function that takes in an array of edges and returns an adjacency list of the graph.
class edge {
int weight, source, dest;
public edge(int source, int dest, int weight) {
this.source = source;
this.dest = dest;
this.weight = weight;
}
}
public static Vector<Vector<edge>> getAdjList(Vector<edge> edges, int n) {
Vector<Vector<edge>> adjList = new Vector<Vector<edge>>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
adjList.add(new Vector<edge>());
}
for(edge e: edges){
adjList.get(e.source).add(e);
adjList.get(e.dest).add(e);
}
return adjList;
}